SOYO 6BA+100 Motherboard
Okay so let’s get on to the real task at hand. Nothing fancy at the overall outlook of the board. Soyo hasn’t forgotten the original layout of the BX boards, and incorporated the same setup as we’re so used to seeing. The board includes 5PCI slots, 2 ISA slots, and One AGP slot. It also includes 4 DIMM slots supporting 1GB of main memory. Right next to the DIMM slots are the IDE cable connectors and Floppy drive connector. The 6BA+100 includes 4 IDE channels, which allow up to 8 IDE devices to be fixed onto the system. (If you have so many in the first place!!)
The right most connectors are the ATA/66/100 IDE connectors. However the manual included has not been revised and it shows it as ATA/66. SOYO does however include a small flyer, which shows the revised diagram of the board. Onto the left of the IDE connectors is the High Point 370 controller. As we mentioned earlier the BX chipset does not support the new ATA/100 protocol. Incorporating this HPT 370 controller enables users to take advantage of this new high-speed protocol.


The 6BA+100 is installed with the 82443BX North Bridge and the 82371 EB South bridge chipset. What disturbed me the most at the initial looks of the board is the overall layout of the components of the board. Notice how close the DIMM slots, the North bridge and the Slot 1 CPU connector are placed.
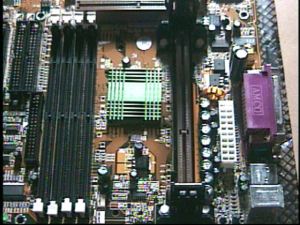
Considering the fact that this board has been designed primarily with overclockers in mind, it is really sad SOYO not thinking of revising the same problem that plagued the 6BA+IV. Initially we tested the board with a Pentium 400 fixed with a VOS 32 cooler. Sadly due to this poor layout the DIMM slot 1 and 2 are rendered useless. We were able to place the memory stick with ease only in DIMM 4. If you plan on overclocking your system extensively you’re bound to get a significantly large cooler. Getting a large HSF means it leaves you with only 1 or in some cases a maximum of 2 DIMM slots (it’ll be a very tight squeeze though). Furthermore there’s no possibility of attaching a cooler to the Northbridge either in case it’s needed. In fact even with the standard CPU cooler the space is not adequate.
This design flaw could be explained by the inclusion of 4 IDE connectors, 4 DIMM slots and trying to fit all that into the PCB. As explained, the 2 extra IDE connectors are required to enable ATA/100 by interfacing it with the HPT 370 controller. Certainly however we cannot justify this design flaw due to this. This might not be a problem to most overclockers out there, however we really do hope SOYO looks into this matter more seriously in future releases.
Another fact that captures our eye is the few number of capacitors around the CPU socket. The 6BA+100 includes eight 1000uF 6.3V capacitors.

The Highpoint HPT370 Controller
BX boards do not have support for ATA/100 interface. Therefore SOYO’s answer to this problem was by installing the board with this High Point 370 controller. This interfaces with the 2 IDE connectors shown here in the picture to give you official support for ATA/100.

The HPT 370 controller also has a built in RIAD controller, which has RAID level 0, level 1 and level 0+1 along with the ability to burst up to 100MB per second.
Before we continue here’s a small word about RAID to all those who are new to this feature.
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a protocol, which is capable of running more than one disk simultaneously. You should however make sure that the drives you use are of the same capacity so that you do not waste space. Some of you might ask why bother with RAID when you could go for one of those high-end SCSI drives. Well folks do you know how much a good SCSI drive cost. Why spend more when you could get similar performance for a cheaper price. Also the fact that the RAID controller is built into this board, the extra cost of buying a RAID controller is also taken care of.
The HPT 370 controller includes support for up to four IDE ATA/100 drives. You could use drives below the ATA/100 mark, since the controller is backward compatible with ATA/66, and ATA/33. Therefore if you haven’t upgraded your machine for a long time and are still holding onto that old IDE drive, you could still use it. However you won’t be able to make use of the burst transfer rate of 100 MB/Sec if this is the case. One fact worth noting is that you could use the two ATA/33 IDE channels even while using the HPT 370, so this effectively gives you a total of 8 drives to your system. Very unlikely that you’ll have at least half this number, nevertheless it’s a feature worthy of consideration.
RAID was a feature that was first introduced to servers. The RAID feature allows each drive in the system to be independent. Therefore in the event one drive fails the other will take over. Due to this high efficient system RAID gathered an incredible popularity. However early RAID technology was limited to only SCSI drives, and only server administrators were really able to afford this. Things have changed now and RAID technology has moved onto IDE drives as well. RAID not only improves the performance of your drive it also increases reliability at the same time. As we mentioned above the HPT 370 controller in this board offers 3 levels of RAID configurations.
Pressing Ctrl + H at the drive detection process will bring up a screen similar to this.
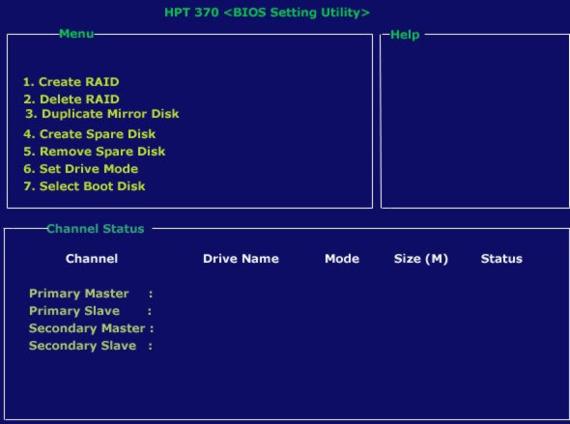
Creating a RAID array is quite simple really. After the above screen is displayed click on “Create RAID”. Thereafter you select the Array mode and the drives you’d like to use. A block size of 64K is recommended. Now click on Create RAID and the RAID array will be setup. Now just simply enjoy its benefits.
RIAD 0 also known as Stripping improves performance by using multiple drives and writing to each in stripes. In RAID 0 level the RAID controller divides the data into equal data blocks. Thereafter it writes even data blocks to one-drive and odd blocks to another. This is how the performance increase is achieved. (It effectively doubles the read/write speed of the drive) There are a few things you should know when implementing RAID 0. RAID 0 is dependent upon the smallest drive’s size you use in your RAID array. Say you have two drives of 45GB and 40GB, then when you implement RAID 0 the total size will be 80GB rather than 85GB. The extra 5GB will be rendered useless. For this reason you should make sure the drives used are of equal size or you waste space for no reason. Another fact that should be looked upon is the choosing of drives. Remember to use two drives of equal performance so that you won’t loose the efficiency of your RAID implementation.
RIAD 1 is known as mirroring. This RAID level is mostly implemented in servers rather than people like us. What RAID 1 does is it creates a mirror image of every thing you do on one drive. So even if you loose one drive the same data can be found in the other. Say for example you copy a 10MB file, the RAID controller will make an exact copy of the file in the other drive. The obvious down side to this is the loss of drive space. If you use two 40GB drives, then after implementing RAID 1 the size will be 40GB total. Even though RAID 1 offers a great deal of reliability, you won’t see me opting for this. Here too the as in RAID 0 the hard drive size issue comes into effect.
As for the board’s I/O connectors it includes the standard 2 COM ports, 2 USB ports, 2 PS/2 connectors (mouse & KB) and a printer port. Just the basic stuff to get you going… nothing fancy or new here. The board also includes 3 FAN connectors; two of them placed right next to the DIMM slots.
These will be quite adequate for all your overclocking needs. Also one fact worth mentioning is that SOYO has uniquely placed the “CMOS Reset” jumper within easy reach after the installation of the board.
Alright folks, that’s about it for the icing of the cake. Let check out to see how well the 6BA+100 performs when it comes to overclocking.